
Top 10 Algebraic Identities with Examples Basic algebra formula YouTube
The last equation is called a trigonometric identity. Solving identity equations: When given an identity equation in certain variables, start by collecting like terms (terms of the same variable and degree) together. Doing this will usually pair terms one on one, thus making it easier to solve. Let's see some examples:

Algebraic Identities Two & Three Variable, Factorization
Algebraic identities play an important role in the mathematics curriculum and in mathematics in general. In Class IX in the Indian secondary school curriculum, eight types of identities are used when solving equations and polynomials. Knowing and recognising these identities helps students to learn mathematical procedures.

ALGEBRAIC IDENTITIES Educational Posters Math Math Poster Etsy UK
Using the list of algebraic formulas from the algebraic identities chart, factorization becomes a streamlined process. Let's explore this with some algebraic examples: Difference of Squares: The identity a. 2. −b. 2 =(a+b)(a−b) can be used to factorize expressions like 9x. 2. −16. Here, a=3x and b=4, so the expression becomes: (3x+4)(3x.

Algebraic Identities Chart Math Formula Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 1869132076
Algebraic Identities Chart. The chart of algebraic identities helps us to understand various types of identities, uses, and applications in algebra and other branches of mathematics. The chart includes: Square of Binomial; Difference Between Squares; Cube of Binomials; Sum of Cubes;
Basic Algebraic Identities Formulae class 8 YouTube
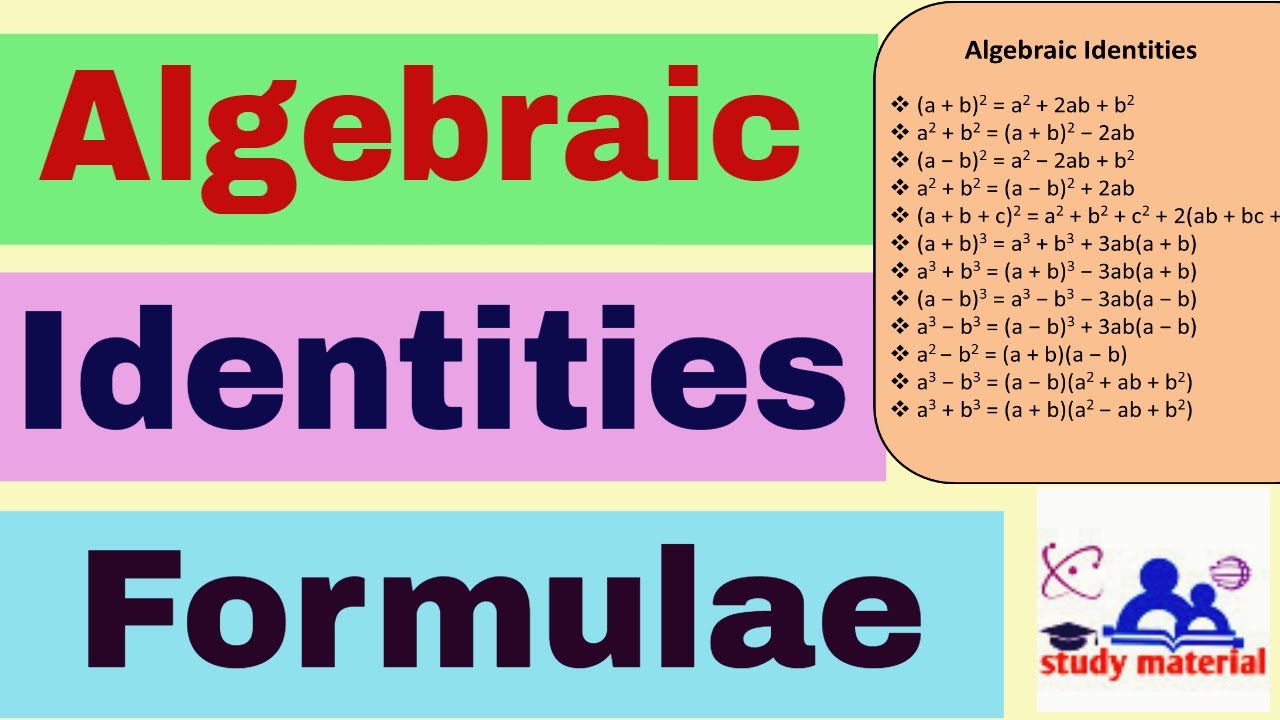
Standard Algebraic Identity 1: Algebraic identity of the square of the summation of two terms is: (a + b)2 = a2 +b2 + 2ab ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 + 2 a b Standard Algebraic Identity 2: Algebraic identity of the square of the difference of two given terms is: (a − b)2 = a2 +b2 − 2ab ( a − b) 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b

Applications of Identities Definition, Types of Algebraic Identities Embibe
Four standard algebraic identities are listed below: Identity-1: Algebraic Identity of Square of Sum of Two Terms (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 Identity-2: Algebraic Identity of Square of Difference of Two Terms (a- b)2 = a2- 2ab + b2 Identity-3: Algebraic Identity of Difference of Two Squares (a + b)(a- b) = a2- b2

Algebraic Identities Definition, Identities, Properties, Examples Embibe Exams
Google Classroom Using identities, evaluate. 99 2 = 5.2 2 = 10.5 × 9.5 = Report a problem Do 10 problems Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.

Algebraic Identities Definition, Identities, Properties, Examples Embibe Exams
Solution: (x 4 - 1) is of the form Identity III where a = x 2 and b = 1. So we have, (x 4 - 1) = ( (x 2) 2 - 1 2) = (x 2 + 1) (x 2 - 1) The factor (x 2 - 1) can be further factorised using the same Identity III where a = x and b = 1. So, (x 4 - 1) = (x 2 + 1) ( (x) 2 - (1) 2) = (x 2 + 1) (x + 1) (x - 1) Eample 3:

Algebraic Identities Working Model Maths Working Model Math Project Model Math TLM Math
This collection of algebraic identities charts emphasizes the derivation of the identity with vivid geometrical representation. Learn the algebraic formulas as a precursor to the simplification of algebraic expressions.

Algebraic Identities with Examples Class 10 part1 YouTube
An identity is a mathematical equation that remains true regardless of the values assigned to its variables. They are useful in simplifying or rearranging algebraic expressions because the two sides of identity are interchangeable, they can be swapped with one another at any point.

Boolean Algebra (HowTo w/ 15 StepbyStep Examples!)
Final answer: Algebraic identities are equations that hold true for all suitable values of its variables. These identities greatly help simplify and solve different algebraic expressions, equations, and problems. Some common identities include the squares and cubes of binomials, difference of squares, and sums and differences of cubes. Explanation:

Free Printable Algebra Formula Chart For Classroom [PDF] Number Dyslexia
An important set of mathematical formulas or equations where the value of the L.H.S. of the equation is equal to the value of the R.H.S. of the equation. Algebraic identities simplify algebraic expressions and calculations. Here are examples of common algebraic identities: ( a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2 a b + b 2 ( a − b) 2 = a 2 − 2 a b + b 2

Algebraic Identities (Part 1) YouTube
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.

Algebraic Identities Chart Math Formula Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 1869814570
An algebraic identifier is an equation where the value of the left-hand side of the equation is equal to the value of the right-hand side of the equation for all variable values. We have several standard identifiers that we can use in different branches of mathematics. All standard Identities are obtained by the Binomial statement.

Algebra Identities Mathematics education, Studying math, Math lessons
Solution: To expand the given expression, substitute a = 2x and b = y in (a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2, (2x + y) 2 = (2x) 2 + 2 (2x) (y) + y 2 = 4x 2 + 4xy + y 2 Three Variable Identities

Algebraic Identities & Proofs Solved Examples & Practice Questions
Algebraic Identities. An algebraic identity is an equality that holds for any values of its variables. For example, the identity (x+y)^2 = x^2 + 2xy + y^2 (x +y)2 = x2 +2xy+y2 holds for all values of x x and y y. Since an identity holds for all values of its variables, it is possible to substitute instances of one side of the equality with the.